The Complete SEO Strategy Guide: Drive Sustainable Organic Growth in 2025
Executive Summary
Search engine optimization remains the cornerstone of digital marketing success. As search algorithms evolve toward greater sophistication, understanding the intersection of technical excellence, content quality, and user experience has never been more critical for businesses seeking sustainable organic growth.
This comprehensive guide synthesizes current best practices, technical requirements, and strategic frameworks necessary for building robust search visibility. Whether you're establishing a new digital presence or refining an existing strategy, the methodologies outlined here provide a evidence-based roadmap for achieving measurable improvements in search performance.

Part I: Foundational Concepts and Search Engine Architecture
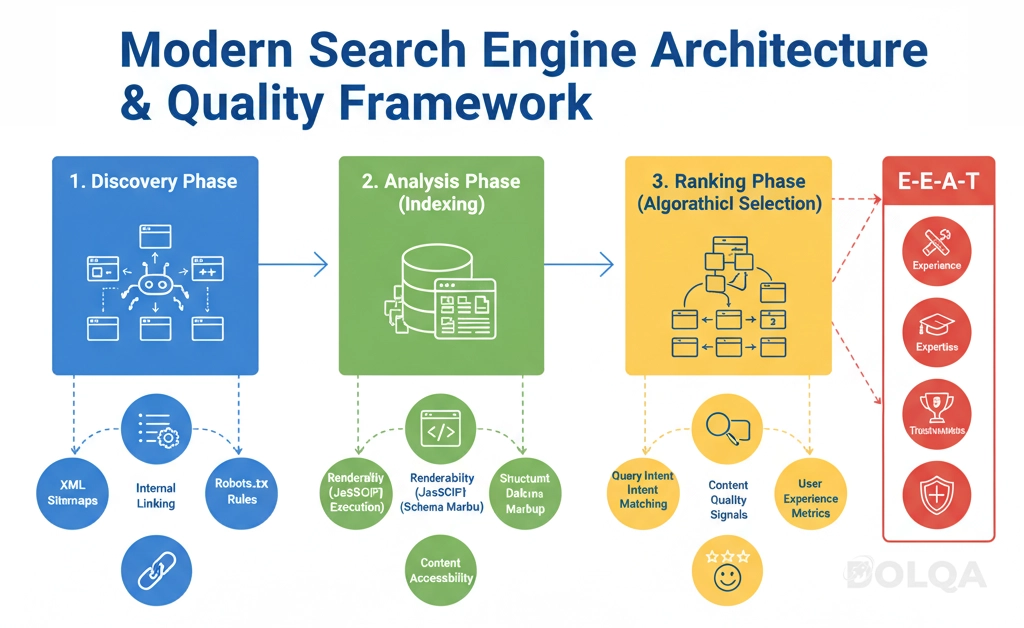
Understanding Modern Search Engine Operations
Contemporary search engines employ sophisticated systems to discover, analyze, and rank billions of web pages. Effective optimization requires understanding three interconnected processes that determine whether your content reaches your target audience.
The Discovery Phase: How Search Engines Find Your Content
Search engines deploy automated programs—commonly referred to as crawlers, spiders, or bots—to systematically discover and map content across the web. Google's primary crawler, Googlebot, navigates the internet by following hyperlinks from known pages to new destinations.
Critical Implementation Elements:
XML Sitemaps: Structured files that catalog your site's important URLs, providing crawlers with an efficient discovery path. Submit sitemaps through Google Search Console to ensure comprehensive coverage.
Robots.txt Configuration: This protocol file instructs crawlers which sections of your site to access or avoid. Misconfiguration can inadvertently block critical resources, so regular auditing is essential.
Internal Link Architecture: A well-structured internal linking system ensures all important pages are discoverable within a reasonable number of clicks from your homepage, facilitating efficient crawling.
The Analysis Phase: Content Indexing and Understanding
Once discovered, search engines must interpret, categorize, and store page content in their index—a massive database that enables rapid query responses.
Key Considerations:
Renderability: Modern search engines must execute JavaScript to fully understand dynamic content. Ensure your site's critical rendering path doesn't block important content from being indexed.
Structured Data: Implementing schema markup helps search engines understand your content's context, entities, and relationships, potentially earning enhanced search result features.
Content Accessibility: Pages must be accessible without requiring user authentication, form submissions, or other barriers that prevent crawler access.
The Ranking Phase: Algorithmic Selection and Ordering
When users submit queries, ranking algorithms evaluate indexed pages against hundreds of factors to determine relevance, quality, and usefulness. Results are ordered based on predicted utility to the searcher.
Current Algorithmic Priorities:
Query Intent Matching: Algorithms classify search intent (informational, navigational, transactional, or commercial investigation) and prioritize content that best satisfies that specific need.
Content Quality Signals: Comprehensive topical coverage, factual accuracy, proper attribution, and demonstration of genuine expertise heavily influence rankings.
User Experience Metrics: Page speed, mobile optimization, visual stability, and overall usability contribute to ranking calculations.
The Quality Framework: E-E-A-T Principles
Google's Search Quality Evaluator Guidelines emphasize four interconnected quality dimensions:
Experience: Demonstrating first-hand, practical experience with the subject matter, particularly important for product reviews, how-to content, and industry-specific guidance.
Expertise: Possessing and demonstrating appropriate knowledge, credentials, or skill level for the topic at hand. The required level varies by subject sensitivity and complexity.
Authoritativeness: Recognition by peers, industry participants, or the broader community as a reliable source on specific topics. Often manifested through citations, references, and inbound links from other authoritative sources.
Trustworthiness: Establishing credibility through accurate information, transparent authorship, secure infrastructure (HTTPS), clear privacy policies, and appropriate contact information.
These principles apply universally but carry heightened importance for YMYL (Your Money or Your Life) content that could impact health, financial stability, safety, or societal welfare.
Part II: Technical Infrastructure and Performance Optimization
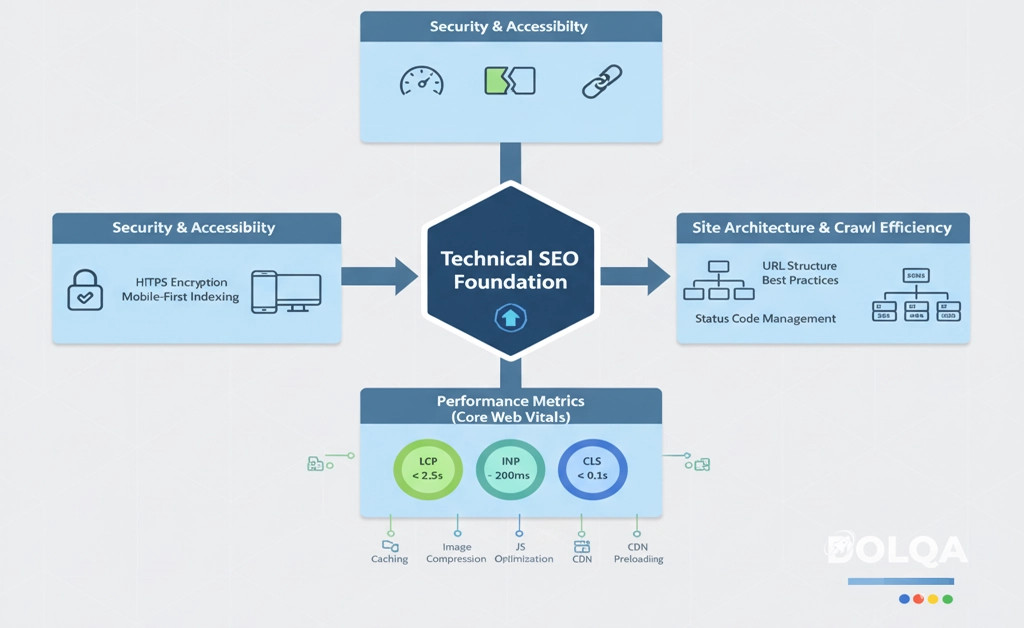
Technical SEO establishes the foundation upon which all other optimization efforts rest. Without proper technical infrastructure, even exceptional content may fail to achieve visibility.
Security and Accessibility Standards
HTTPS Implementation: Transport Layer Security (TLS) encryption is non-negotiable. Beyond being a confirmed ranking signal, HTTPS establishes user trust and protects data integrity. Obtain certificates from reputable Certificate Authorities and ensure proper implementation across all site resources.
Mobile-First Indexing: Google predominantly uses mobile versions of content for indexing and ranking. Responsive design is insufficient—your mobile experience must deliver equivalent functionality, content, and usability as desktop versions.
Performance Metrics and Core Web Vitals
Page experience significantly impacts both user satisfaction and search performance. Google's Core Web Vitals provide quantifiable metrics for measuring real-world user experience:
Largest Contentful Paint (LCP): Measures loading performance by tracking when the largest content element becomes visible. Target: under 2.5 seconds.
Interaction to Next Paint (INP): Replaces First Input Delay to measure overall responsiveness throughout the page lifecycle. Target: under 200 milliseconds.
Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS): Quantifies visual stability by measuring unexpected layout shifts during page load. Target: under 0.1.
Optimization Strategies:
- Implement efficient caching policies for static resources
- Optimize image delivery through modern formats (WebP, AVIF) and responsive serving
- Minimize JavaScript execution time and reduce main thread blocking
- Utilize Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) for improved geographic distribution
- Implement preloading for critical resources and prefetching for anticipated navigation
Site Architecture and Crawl Efficiency
URL Structure Best Practices: Construct descriptive, hierarchical URLs that communicate page purpose and site structure. Use hyphens as word separators, maintain consistent case (lowercase preferred), and avoid unnecessary parameters.
Canonical URL Management: Prevent duplicate content issues by specifying canonical versions for pages accessible through multiple URLs. Implement canonical tags, manage URL parameters in Search Console, and maintain consistent internal linking patterns.
Status Code Management: Ensure proper HTTP status code implementation—particularly 404 (Not Found), 301 (Permanent Redirect), and 302 (Temporary Redirect)—to guide crawler behavior and preserve link equity during site changes.
Part III: Content Development and On-Page Optimization
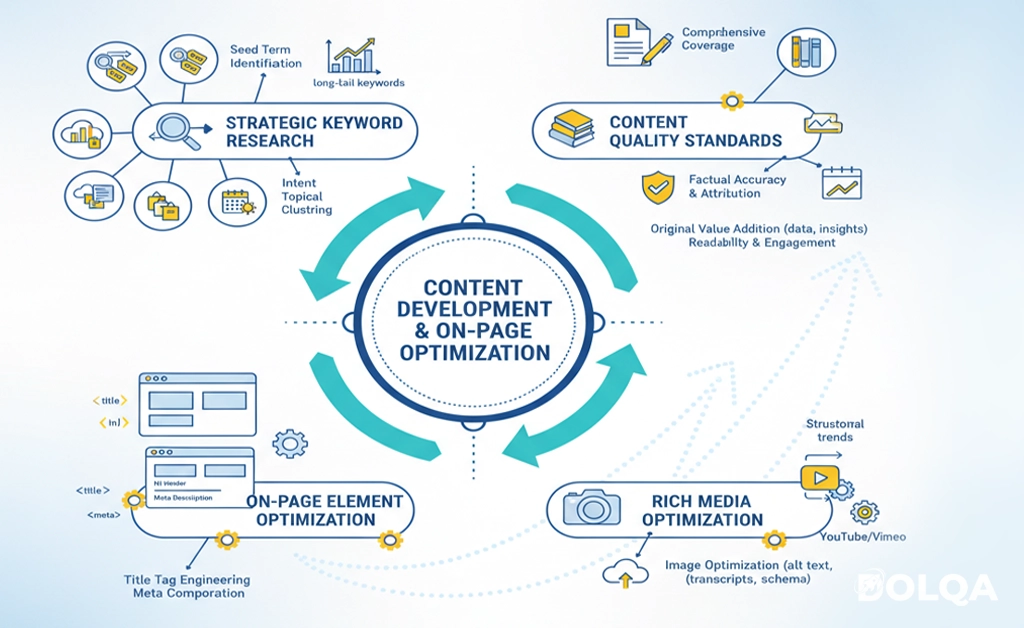
Content quality remains the most significant controllable ranking factor. Strategic content development requires understanding user needs, competitive landscapes, and topical authority building.
Strategic Keyword Research Methodology
Effective keyword research extends beyond search volume analysis to encompass competitive assessment, commercial intent, and topical clustering.
Research Framework:
- Seed Term Identification: Begin with core topics relevant to your expertise and business objectives
- Expansion and Variation: Identify semantic variations, question-based queries, and long-tail opportunities
- Intent Classification: Categorize keywords by search intent to ensure appropriate content format matching
- Competitive Analysis: Assess ranking difficulty by analyzing current top-ranking pages' authority and content quality
- Topical Clustering: Group related keywords into content clusters that collectively establish topical authority
Advanced Considerations:
- Search volume should inform priority but not exclusively determine targeting decisions
- Long-tail, lower-volume queries often demonstrate higher conversion intent
- Consider seasonal trends and emerging topics in growing industries
- Analyze "People Also Ask" sections and related searches for content expansion opportunities
Content Quality Standards
Comprehensive Coverage: Thoroughly address the target topic from multiple relevant angles. Surface-level treatment rarely achieves competitive rankings in established spaces.
Factual Accuracy and Attribution: Verify claims through authoritative sources, link to supporting evidence, and correct errors promptly when identified. Accuracy builds trust with both users and search engines.
Original Value Addition: Differentiate your content through:
- Proprietary research or data analysis
- Expert commentary from credentialed professionals
- Unique perspectives informed by direct experience
- More current information than existing resources
- Superior organization, clarity, or comprehensiveness
Readability and Engagement: Structure content for scanability with descriptive headings, logical paragraph breaks, relevant visuals, and varied content formats (text, images, videos, interactive elements) that maintain reader attention.
On-Page Element Optimization
Title Tag Engineering: The title tag remains the strongest on-page ranking signal. Effective titles:
- Include primary target keywords near the beginning
- Accurately reflect page content
- Differentiate from competing results through unique value propositions
- Stay within 50-60 character limits to prevent truncation
- Balance optimization with compelling copy that drives clicks
Meta Description Composition: While not directly affecting rankings, meta descriptions significantly influence click-through rates. Compelling descriptions:
- Summarize page value proposition concisely
- Include relevant keywords (which appear bolded in results)
- Incorporate clear calls-to-action when appropriate
- Maintain 150-160 character lengths for full display
- Align with title tag messaging for consistency
Heading Hierarchy Optimization: Proper heading structure (H1-H6) serves both organizational and optimization functions:
- Use a single, descriptive H1 per page
- Structure content logically with H2s for major sections and H3s for subsections
- Incorporate target and related keywords naturally within headings
- Ensure headings accurately describe following content
- Maintain proper hierarchical nesting
Rich Media Optimization
Image Optimization Protocol:
- Implement descriptive, keyword-relevant alt attributes for accessibility and context
- Use descriptive file names before uploading (seo-strategy-diagram.jpg vs. IMG_1234.jpg)
- Compress images without quality degradation using tools like ImageOptim or Squoosh
- Implement responsive image serving (srcset attribute) for appropriate sizing
- Consider lazy loading for below-fold images to improve initial page speed
Video Content Integration:
- Host on appropriate platforms (YouTube, Vimeo) for optimal delivery
- Provide descriptive titles, descriptions, and tags
- Include video transcripts for accessibility and keyword coverage
- Implement video schema markup for enhanced search appearance
- Create custom thumbnails that encourage engagement
Part IV: Authority Building and Off-Site Signals
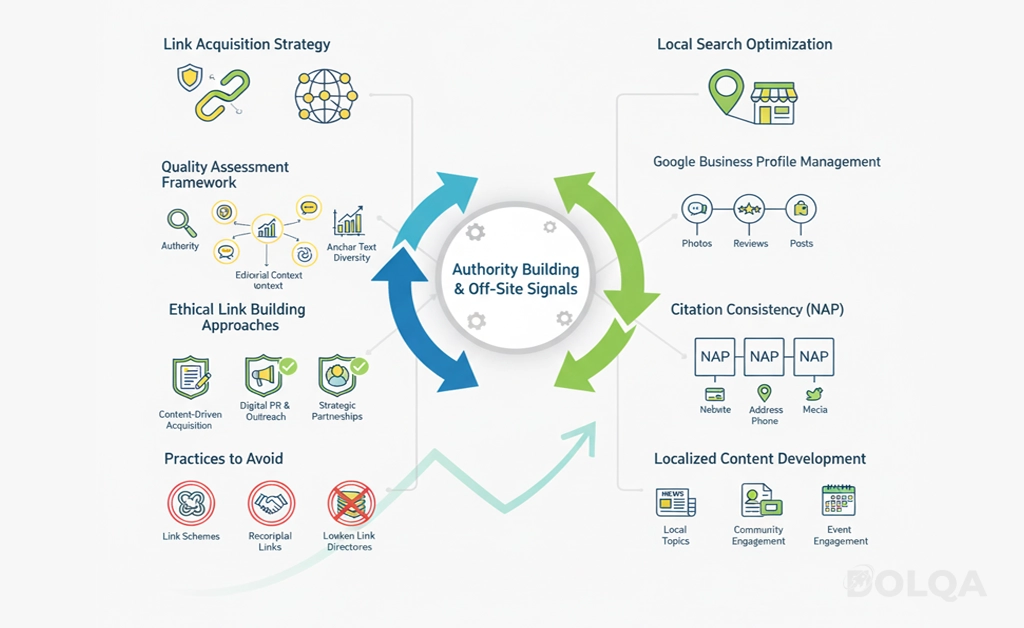
Off-site factors—primarily backlinks—remain critical for establishing topical authority and competitive rankings, particularly in contested spaces.
Link Acquisition Strategy
Quality Assessment Framework: Evaluate potential linking sources across multiple dimensions:
- Relevance: Links from topically related sites carry greater weight
- Authority: Source site's own backlink profile and ranking performance
- Traffic: Links from actively visited sites provide direct referral value beyond SEO benefits
- Editorial Context: Links within relevant, substantive content outperform sidebar or footer placements
- Anchor Text Diversity: Natural link profiles contain varied anchor text, not repetitive exact-match keywords
Ethical Link Building Approaches:
Content-Driven Acquisition: Create genuinely linkworthy assets (original research, comprehensive guides, unique tools, industry studies) that naturally attract editorial links
Digital PR and Outreach: Develop newsworthy stories, expert commentary, or data-driven insights that appeal to journalists and industry publications
Strategic Partnerships: Collaborate with complementary businesses, industry associations, and educational institutions for mutually beneficial linking opportunities
Expert Contributions: Author guest articles, participate in expert roundups, or provide quotes for industry publications (ensure these provide genuine value, not thin promotional content)
Broken Link Replacement: Identify broken links on relevant sites and offer your content as a superior replacement
Practices to Avoid: Link schemes, reciprocal linking networks, low-quality directory submissions, paid links without proper attributes (nofollow/sponsored), and automated link building all violate search engine guidelines and risk penalties.
Local Search Optimization
For businesses with physical locations or service areas, local search represents significant opportunity:
Google Business Profile Management:
- Complete all profile sections thoroughly and accurately
- Select appropriate business categories (primary and secondary)
- Add high-quality photos regularly
- Respond to all reviews professionally and promptly
- Post updates, offers, and events consistently
Citation Consistency: Ensure NAP (Name, Address, Phone) information matches exactly across:
- Your website
- Google Business Profile
- Social media profiles
- Industry directories and review sites
- Local business associations
Localized Content Development: Create content addressing local topics, events, and community involvement to strengthen local relevance signals.
Part V: Analytics, Measurement, and Continuous Optimization
Effective SEO requires systematic measurement, analysis, and iterative improvement based on performance data.
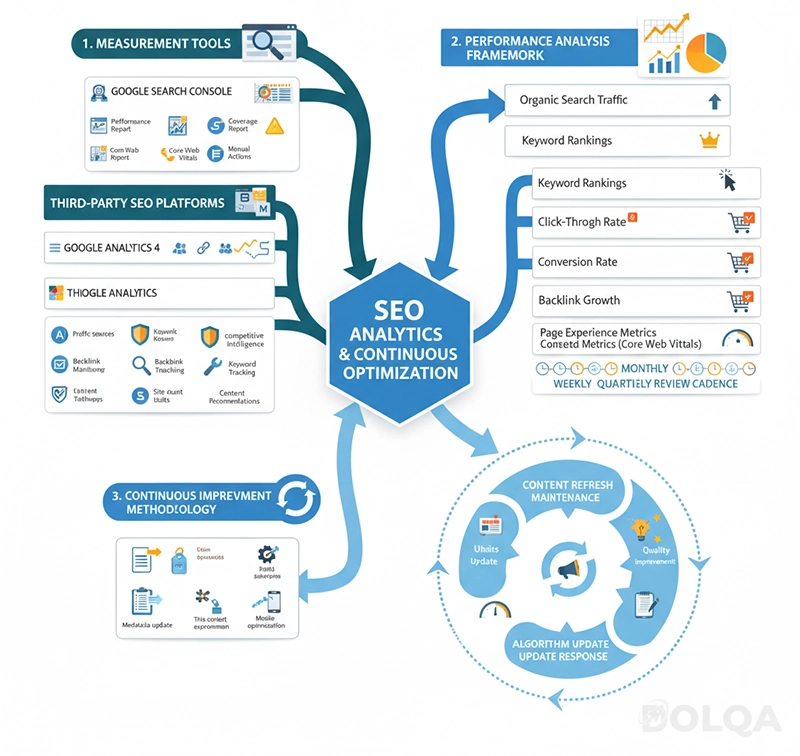
Essential Measurement Tools
Google Search Console: Your primary window into how Google views your site. Critical reports include:
- Performance Report: Track impressions, clicks, click-through rates, and average position by query, page, and date
- Coverage Report: Identify indexing issues, validation status, and sitemap problems
- Core Web Vitals Report: Monitor page experience metrics across your site
- Manual Actions: Receive notifications of any guideline violations
Google Analytics 4: Understand user behavior post-click:
- Traffic sources and acquisition channels
- User engagement metrics (session duration, pages per session, bounce rate)
- Conversion tracking and goal completion
- Audience demographics and interests
- Content performance and user pathways
Third-Party SEO Platforms: Consider tools like Ahrefs, SEMrush, or Moz for:
- Competitive intelligence and gap analysis
- Comprehensive backlink monitoring
- Keyword ranking tracking across locations
- Site audit automation
- Content optimization recommendations
Performance Analysis Framework
Key Performance Indicators:
- Organic Search Traffic: Total sessions from organic search, segmented by landing page and keyword
- Keyword Rankings: Position tracking for target terms, particularly those with commercial value
- Click-Through Rate: Percentage of impressions converting to clicks in search results
- Conversion Rate: Percentage of organic visitors completing desired actions
- Backlink Growth: Rate of new referring domains and total backlinks acquired
- Page Experience Metrics: Core Web Vitals performance across key landing pages
Analysis Cadence: Review performance weekly for tactical adjustments, monthly for strategic assessment, and quarterly for comprehensive audits and planning.
Continuous Improvement Methodology
- Audit existing content quarterly to identify refresh opportunities
- Update statistics, examples, and screenshots to maintain currency
- Expand thin content to improve comprehensiveness
- Consolidate overlapping content to prevent cannibalization
- Update metadata to improve click-through rates
Technical Maintenance:
- Monitor crawl errors and fix broken links promptly
- Review page speed regularly and address performance degradation
- Update structured data as schema standards evolve
- Ensure mobile experience remains optimal as site evolves
Algorithm Update Response:
- Monitor official Google channels for confirmed updates
- Analyze traffic patterns for correlation with known updates
- Resist knee-jerk reactions; evaluate changes over weeks, not days
- Focus on fundamental quality improvements rather than algorithmic manipulation
- Document changes and their impacts for institutional knowledge
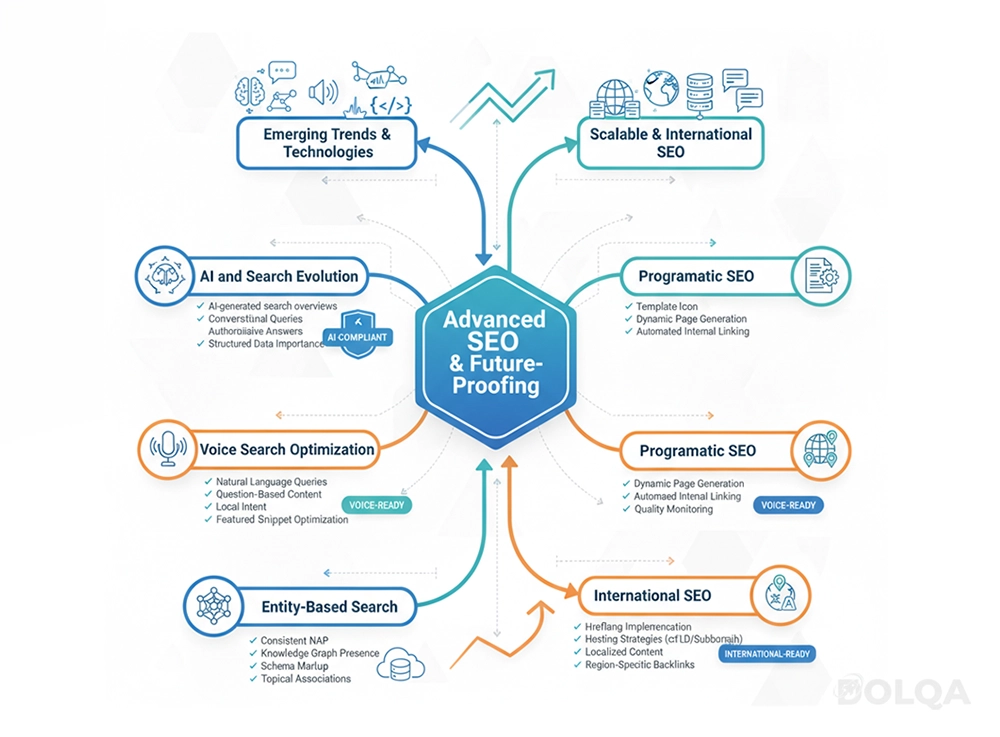
Part VI: Advanced Considerations and Future-Proofing
Emerging Trends and Technologies
AI and Search Evolution: Generative AI is transforming search behavior and result formats. Optimization strategies must account for:
- AI-generated overviews in search results
- Conversational query patterns
- Emphasis on direct, authoritative answers
- Importance of structured data for information extraction
Voice Search Optimization: As voice-activated devices proliferate, consider:
- Natural language query patterns
- Question-based content structuring
- Local intent in voice queries
- Featured snippet optimization for voice results
Entity-Based Search: Search engines increasingly understand entities (people, places, things, concepts) and their relationships. Build entity authority through:
- Consistent NAP information across the web
- Knowledge Graph presence (Wikipedia, Wikidata)
- Structured data implementation (schema.org markup)
- Building topical associations through consistent content themes
Scalable SEO for Enterprise Organizations
Programmatic SEO: For sites with large inventories or databases:
- Develop template-based approaches for similar page types
- Implement dynamic content generation while maintaining quality
- Create scalable internal linking through automated relationship identification
- Monitor for quality issues through sampling and automated checks
International SEO: For multi-language or multi-regional sites:
- Implement proper hreflang annotations
- Consider hosting decisions (ccTLDs, subdomains, subdirectories)
- Ensure content is properly localized, not just translated
- Build region-specific backlinks and citations
Conclusion: Strategic Fundamentals for Long-Term Success
Search engine optimization remains dynamic, with algorithms continuously evolving to better serve user needs. However, core principles endure: create genuinely valuable content, maintain technical excellence, build authentic authority, and prioritize user experience above all else.
Success in SEO requires patience, consistency, and commitment to quality over shortcuts. The strategies outlined in this guide provide a comprehensive framework for building sustainable organic visibility, but implementation requires adaptation to your specific context, audience, and resources.
Focus your efforts on understanding your audience deeply, addressing their needs thoroughly, and building genuine expertise and authority in your field. These fundamentals remain constant regardless of algorithmic changes and will continue driving results far into the future.







Comments (0)
Leave a Comment
No comments yet. Be the first to comment!